Once they strike, they can cause massive economic losses and casualties, affecting vast areas. This often leads people to wonder: How do earthquakes actually occur? Why do earthquakes occur? What should we do when an earthquake strikes? When an earthquake strikes, human existence becomes insignificant. Therefore, it's important to learn more about geography and acquire survival tips to protect ourselves as best we can when an earthquake strikes.

Causes of Earthquakes
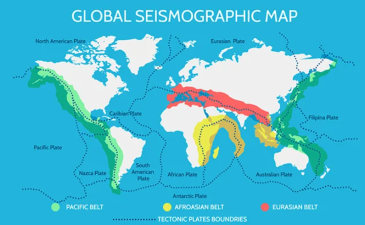
The fundamental cause of earthquakes lies in Earth's internal tectonic plates and plate movement. The rock formations on Earth's surface aren't a single solid mass, but rather consist of dozens of large and small plates. Tectonic movements cause earthquakes when these plates collide, rub, separate, or slide against each other.
- Plate Movement
The Earth's crust is composed of several large plates, which are not static but in constant motion. The plates, driven by the mantle, move horizontally and vertically. For example, the collision of the Eurasian and Indian plates led to the formation of the Himalayas, accompanied by large-scale earthquake activity. 2. Faults within the Earth's crust
Faults on the Earth's surface are another major factor contributing to earthquakes. Faults are fractures in rock layers, typically between two rocks. When underground pressure becomes excessive, these rocks can slip along the faults, releasing the enormous energy stored in them and triggering earthquakes.
- Volcanic activity
Volcanic eruptions can also cause earthquakes. When magma rises to the surface, it can force fractures in the Earth's crust, generating tremors. Furthermore, earthquakes in volcanically active areas are often accompanied by volcanic eruptions.
- Human activity
Some human activities, such as mining, underground nuclear testing, and large dam construction, can also trigger earthquakes. These activities alter the distribution of underground pressure, causing rocks to fracture or slip.
Earthquakes are divided into two categories:
Internal (or internally induced) earthquakes
Earthquakes caused by forces generated by internal Earth activity are called internal earthquakes, such as the traditional categories of tectonic earthquakes and volcanic earthquakes.
External (or externally induced) earthquakes
Earthquakes caused by forces generated by external Earth activity are called external earthquakes, such as the traditional categories of collapse earthquakes, induced earthquakes, and meteorite impact earthquakes. Changes Before an Earthquake
Before an earthquake, some natural phenomena undergo unusual changes. These changes are intrinsically linked to the occurrence of an earthquake and are also called earthquake precursors.
Earthquake precursors include:
① Abnormal local changes in the strength and declination of the Earth's magnetic field*;
② Ground rise and fall, horizontal displacement, and tilt;
③ Abnormal values of the earth's current* or the natural potential difference between any two points;
④ Abnormalities in water levels, smell, color, clarity, or the presence of bubbles;
⑤ Unusual reactions to some animals;
⑥ Earthquake sounds, which can vary, such as muffled thunder, howling winds, and cracking rocks. An earthquake will occur shortly after these sounds;
⑦ Before and after an earthquake, especially in the moments before it occurs, luminous phenomena often appear above the earthquake area.
Changes After an Earthquake
Cracks appear in the ground, causing depressions and uplifts, which can trigger tsunamis, landslides, and building collapses.
What should I do when an earthquake strikes?
- Don't panic when an earthquake strikes; respond immediately.
When an earthquake strikes, cities generally fall into panic, but this panic is the key to fatalities.
After an earthquake strikes, it's crucial to follow the three principles of lying down, taking cover, and holding on. This can save your life in a critical moment.
- Avoid danger regardless of main shocks or aftershocks.
When avoiding danger, people often take a chance and fail to take shelter when aftershocks occur. This is actually the most fatal factor, as aftershocks can occur at any time and beyond people's expectations.